DVS Heat Transfer Systems: A Definitive Guide to Smarter IoT Integration
Wiki Article
A Comprehensive Guide to Selecting the Right Heat Transfer Solutions for Your Requirements
Choosing the ideal Heat transfer system is essential for functional effectiveness. Numerous systems satisfy different needs, affected by variables such as temperature level variety and liquid kind. Understanding the concepts behind Heat transfer, such as convection, radiation, and transmission, is critical. Furthermore, assessing power sources and upkeep techniques can affect long-lasting efficiency. A closer exam of these considerations exposes how to tailor a system to certain demands. What should one prioritize in this facility decision-making procedure?Recognizing Heat Transfer: Key Concepts and Principles
Heat transfer might seem like a simple principle, it incorporates a variety of principles that are fundamental for efficient system layout - DVS Heat Transfer Systems. Recognizing these principles is essential for engineers and designers that aim to maximize thermal performance in various applications. Conduction, for circumstances, includes the transfer of Heat through solid products, while convection refers to the motion of Heat within liquids. Radiation, one more vital principle, defines how Heat can be moved via electromagnetic waves. Each of these devices plays a vital function in determining exactly how energy moves within a system. By extensively realizing these ideas, experts can make informed decisions, ensuring that Heat transfer systems run effectively and meet the specific needs of their applications
Types of Heat Transfer Systems: A Summary
Comprehending the concepts of Heat transfer prepares for exploring the various kinds of Heat transfer systems available. Heat transfer systems can be classified primarily right into 3 kinds: radiation, conduction, and convection. Transmission involves Heat transfer with strong materials, depending on direct call between fragments. Convection, on the various other hand, occurs in fluids (liquids and gases) where the motion of the liquid itself assists in Heat transfer. Radiation includes the transfer of Heat with electro-magnetic waves and does not require a medium, enabling it to happen in a vacuum cleaner. Each sort of system has unique characteristics and applications, making it essential for individuals and organizations to very carefully evaluate their certain requirements when selecting one of the most appropriate Heat transfer option.Applications of Heat Transfer Solutions in Various Industries
Heat transfer systems play a necessary role throughout different markets, influencing effectiveness and product quality. In industrial manufacturing procedures, they assist in accurate temperature control, while in food and beverage processing, they assure safety and security and preservation. Furthermore, heating and cooling and climate control systems rely heavily on efficient Heat transfer to maintain comfortable environments.Industrial Manufacturing Processes

Many industrial production procedures depend greatly on reliable Heat transfer systems to make best use of performance and enhance product top quality. In sectors such as metalworking, Heat exchangers play an essential duty in maintaining suitable temperature levels throughout welding, spreading, and creating. These systems assure uniform Heat circulation, which is crucial for achieving desired product residential or commercial properties. In the chemical production industry, Heat transfer systems promote accurate temperature control during reactions, affecting yield and safety. Additionally, in fabric production, reliable Heat administration is necessary for coloring and completing procedures, influencing shade consistency and fabric high quality. By choosing proper Heat transfer innovations, manufacturers can boost energy effectiveness and decrease functional prices, ultimately resulting in a more lasting and competitive manufacturing environment.
Food and Drink Processing
Effective Heat transfer systems are equally crucial in the food and drink processing industry, where preserving suitable temperatures is essential for food safety and quality. These systems play a necessary role in procedures such as sterilization, food preparation, and pasteurization, ensuring that products are secure for consumption and maintain their nutritional worth. Heat exchangers, for circumstances, successfully transfer Heat in between fluids, enhancing power usage while minimizing temperature variations. Additionally, refrigeration systems are fundamental for maintaining perishable products and extending service life. The option of Heat transfer technology directly affects operational performance and product stability, making it critical for food and drink suppliers to select the ideal systems customized to their specific processing needs. This careful selection eventually adds to customer satisfaction and food safety.
A/c and Climate Control
While lots of industries depend on Heat transfer systems for performance, HEATING AND COOLING (Home Heating, Ventilation, and Cooling) plays a crucial function in keeping interior climate control throughout numerous settings. These systems utilize Heat transfer principles to control temperature, air, and moisture high quality, guaranteeing convenience and safety and security in property, business, and commercial atmospheres. Properly created HVAC systems improve power performance, reduce operational costs, and lessen ecological impact. In industrial buildings, for example, reliable environment control adds to staff member productivity and client contentment. In industrial applications, heating and cooling systems assist preserve ideal conditions for devices operation and product preservation. Selecting the best Heat transfer system is important for meeting certain environment control requirements and achieving overall system performance.Assessing Energy Resources for Heat Transfer Equipments
In reviewing power resources for Heat transfer systems, a comparison of renewable power alternatives and fossil gas factors to consider is vital. Eco-friendly resources, such as solar and wind, offer sustainable alternatives that can minimize ecological effect. On the other hand, fossil fuels remain common due to their recognized infrastructure and power density, triggering a careful assessment of both alternatives.Renewable Power Options

Nonrenewable Fuel Source Considerations
Reviewing nonrenewable fuel source factors to consider is essential for the performance and sustainability of Heat transfer systems. Fossil fuels, such as all-natural gas, oil, and coal, are standard energy sources that provide substantial Heat output, making them preferred options for industrial and residential applications. Their environmental influence, including greenhouse gas exhausts and resource deficiency, increases concerns. When selecting a warmth transfer system, it is important to analyze the schedule, expense, and regulatory elements connected with these fuels. In addition, the efficiency of nonrenewable fuel source systems should be considered, as higher performance can reduce some ecological drawbacks. Inevitably, a well balanced approach evaluating efficiency and sustainability can guide decision-makers toward the most proper Heat transfer service for their details requirements.Factors to Consider When Choosing a Warmth Transfer System
Picking a suitable Heat transfer system calls for cautious factor to consider of various elements that can substantially influence efficiency and performance. One vital element is the operating temperature array, which determines the materials and design appropriate for the application. In addition, the type of liquid used in the system-- whether gas or liquid-- affects Heat transfer effectiveness and compatibility. The system's dimension and capability have to straighten with the specific needs of the operation to prevent inadequacies. Power source availability is likewise crucial, affecting operating expense and sustainability. Furthermore, the installment environment, including room constraints and accessibility for upkeep, plays a significant role in system selection. Finally, regulatory compliance and safety and security criteria have to be taken into consideration to ensure the system satisfies all legal requirements.Upkeep and Performance Optimization for Heat Transfer Systems
Keeping Heat transfer systems is vital for guaranteeing maximum efficiency and longevity. Normal upkeep activities, such as cleansing Heat exchangers and examining insulation, help protect against performance losses because of fouling and thermal bridging. Additionally, keeping track of system criteria, consisting of pressure and temperature level, allows for very early detection of abnormalities, reducing downtime and pricey repair services. Implementing a preventative maintenance timetable can optimize efficiency and extend the life-span of components. Upgrading to sophisticated control systems can boost operational performance by changing to differing conditions and lots. By prioritizing maintenance and performance optimization, operators can accomplish lowered energy usage, reduced functional costs, and enhanced total system reliability, eventually bring about better resource use and an extra sustainable operation.Future Patterns in Heat Transfer Technologies
As industries progressively focus on sustainability and energy efficiency, future patterns in Heat transfer technologies are established to undergo considerable transformations. Advancements such as innovative materials, including carbon nanotubes and nanofluids, promise improved thermal conductivity and effectiveness. In addition, the assimilation of renewable energy sources into Heat transfer systems is acquiring momentum, advertising eco-friendly solutions. Smart innovations, including IoT sensors, are expected to reinvent surveillance and control, allowing real-time information evaluation for enhanced efficiency. Additionally, the advancement of modular and compact systems will facilitate easier installment and upkeep, accommodating diverse applications. These improvements suggest a shift towards more sustainable, efficient, and adaptable Heat transfer options, lining up with global energy objectives and ecological criteria.
Often Asked Questions
What Are the Ecological Effects of Heat Transfer Equipments?
The ecological impacts of Heat transfer systems can include greenhouse gas emissions, power usage, and potential thermal air pollution. Furthermore, improper disposal of inefficiencies and products can add to source exhaustion and community disturbance.Exactly how Do I Calculate the Cost-Effectiveness of a Warmth Transfer System?
To calculate the cost-effectiveness of a warmth transfer system, one should assess preliminary costs, functional expenses, maintenance requirements, and power effectiveness, comparing these variables against the anticipated life expectancy and efficiency of the system.Can Heat Transfer Equipment Be Made Use Of in Residential Settings?
Heat transfer systems can certainly be utilized in residential setups. They offer reliable home heating and cooling options, making homes more comfy while potentially lowering energy prices. Their adaptability enables various applications in property settings.What Safety Laws Relate To Heat Transfer Systems?
Security laws for Heat transfer systems generally consist of standards on procedure, upkeep, and installment. Compliance DVS Heat Transfer Systems with regional building codes, maker requirements, and industry standards is vital to guarantee safe and efficient system performance in various applications.How Do Different Materials Affect Heat Transfer Efficiency?
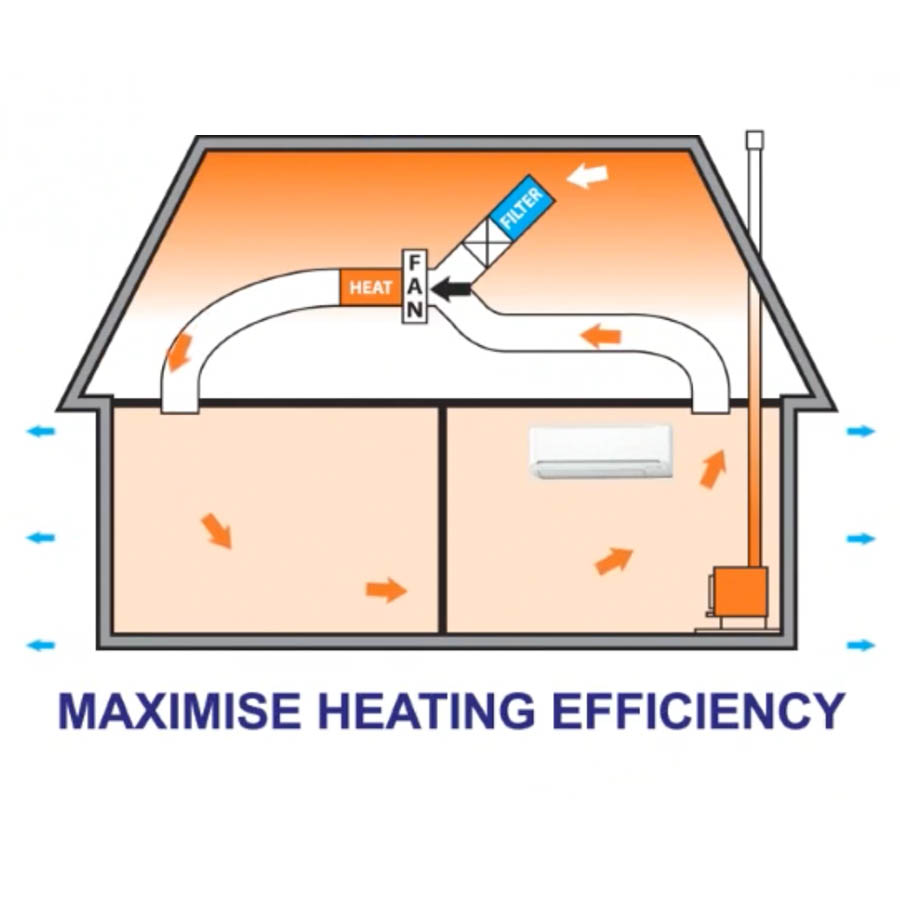
Conduction, for instance, entails the transfer of Heat through strong products, while convection refers to the movement of Heat within liquids. Understanding the principles of Heat transfer lays the foundation for exploring the different kinds of Heat transfer systems available. Heat exchangers, for circumstances, successfully transfer Heat in between fluids, enhancing energy usage while minimizing temperature changes. In reviewing energy sources for Heat transfer systems, a contrast of eco-friendly power options and fossil fuel considerations is crucial. Steels, such as copper and aluminum, conduct Heat efficiently, whereas insulators like rubber and glass reduce down Heat circulation.
Report this wiki page